ESR blog
Shiv Vasa, Ramesha Wishna-Kadawarage, Pauline Lichou
The term microbiomeThe diverse consortium of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, viruses, and their collective genome f… describes the totality of microbes, including their genetic material, living in a particular environment. This consortium of microbes is composed of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa and viruses. However, often the term microbiomeThe diverse consortium of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, viruses, and their collective genome f… refers only to bacteria. Specific terms exist to refer to specific microbes, such as the virome or the mycobiome, which include all viruses and fungi, respectively. The microbiomeThe diverse consortium of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, viruses, and their collective genome f… occupies any surface of an animal exposed to the external environment and therefore covers the skin, genital, respiratory and gastro-intestinal tracts (GITThe part of the digestive system that consists of the stomach and intestines.). The GITThe part of the digestive system that consists of the stomach and intestines. of animals, harbors a diversity of microbes. A healthy gut microbiomeCollective genetic material of the microbes (for example bacteria, fungi and viruses) that live insi… plays an important role in host gut development and physiology, immunomodulation, pathogen exclusion, resilience to stress factors such as weaning and heat stressA condition when animals do not have the ability to withstand high ambient temperatures especially w… and brain health through the gut-brain axis. An imbalance in the microbiomeThe diverse consortium of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, viruses, and their collective genome f… composition is known also as dysbiosis and may negatively affect the aforementioned traits and ultimately animal performance.
The mammalian GITThe part of the digestive system that consists of the stomach and intestines. is populated by trillions of bacteria. For instance, the colon alone is populated by 1010 and 1011 bacteria. These are in constant interaction with the host and other members of the microbial community. Early gut colonization of microbiota in a piglet life is vital. Many scientific studies have proved this by raising piglets in sterile (germ-free) environment and comparing them to microbial exposed piglets. The sterile piglets failed to have optimal early gut microbial colonization and hence had reduced gut barrier function, mucus production and suffered from inadequate intestinal epithelium functioning. Early microbial colonization also has later life consequences in the weaner and finisher stages. For example, piglets experiencing diarrhea post weaning had different microbiomeThe diverse consortium of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, viruses, and their collective genome f… than non-diarrheic pigs, even from one day after birth. Additionally, there is sufficient evidence, which suggests an impact of gut microbial diversity on growth and feed efficiencyA cumulative efficiency with which livestock like the pig or the broiler utilizes dietary nutrients …, especially in finisher pigs.
Therefore, modulating the gut microbiomeCollective genetic material of the microbes (for example bacteria, fungi and viruses) that live insi… by targeted strategies at the early-life colonization has potential to improve gut development, growth performance and overall health in pigs. In our projects within the MonoGutHealth project, we are investigating such strategies. For instance, Kevin Bogota (ESR7) administers a multicomponent plant cocktail to weaners and broilersChickens kept for meat production. Fast growing breeds can reach a weight of over 2 kg at 5 weeks of… to reduce post-weaningPeriod after the piglets are separated (weaned) from the sows. diarrhea and optimize gut health. Moreover, Shiv Vasa (ESR9) and Pauline Lichou (ESR10) investigate if modifying sow gut microbiomeCollective genetic material of the microbes (for example bacteria, fungi and viruses) that live insi… can influence piglet gut colonization by supplementing sow diet with probioticsLive microbial feed supplements, which beneficially affects the host animal by improving its intesti… and other feed additivesProducts used in animal nutrition to achieve an effect on the feed itself, on the animals, on food p….
Similarly, the chicken gut also hosts a variety of microbes where the composition and quantity are influenced by many factors such as age, diet, housing conditions and site of the GITThe part of the digestive system that consists of the stomach and intestines.. Apart from the major functions of gut microbiomeCollective genetic material of the microbes (for example bacteria, fungi and viruses) that live insi… described above, the gut microbiomeCollective genetic material of the microbes (for example bacteria, fungi and viruses) that live insi… of chickens displays a crucial role in influencing the bird’s ability to cope with heat stressA condition when animals do not have the ability to withstand high ambient temperatures especially w…. The chicken gut is also known to carry food born pathogens such as CampylobacterA common bacteria present in poultry gut causing little to no clinical symptoms. and Salmonella strains which cause gastroenteritis in humans. Hence, gut microbiomeCollective genetic material of the microbes (for example bacteria, fungi and viruses) that live insi… modulation in chickens is vital to ensure the health and welfare of birds as well as food safety of the poultry products. Ramesha Wishna-Kadawarage (ESR3) and Modou Mangan (ESR4) work on gut microbiota modulation by delivering bioactivesBiologically active compounds, which might have positive impact on biological processes in organisms… in-ovoA Latin term to say “inside the egg”. It can also mean the embryonic development stage in poultr… to minimize the colonization of pathogens in the GITThe part of the digestive system that consists of the stomach and intestines. and heat stressA condition when animals do not have the ability to withstand high ambient temperatures especially w… effects on broilersChickens kept for meat production. Fast growing breeds can reach a weight of over 2 kg at 5 weeks of…, respectively. Additionally, Muhammad Zeeshan Akram (ESR11) works on the impact of different hatching systems on the microbiomeThe diverse consortium of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, viruses, and their collective genome f… of broilersChickens kept for meat production. Fast growing breeds can reach a weight of over 2 kg at 5 weeks of…. Thus, the various PhD projects within the MonoGutHealth project seek to utilize the modulation potential of the gut microbiomeCollective genetic material of the microbes (for example bacteria, fungi and viruses) that live insi… to address major issues in pig and poultry production.
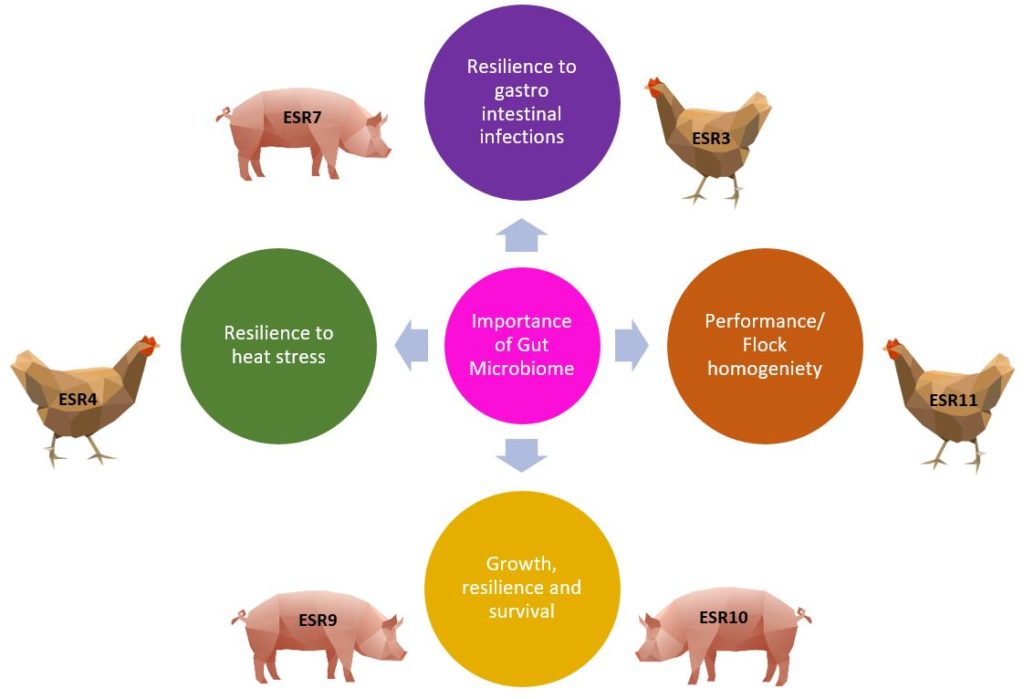
The objective of the MonoGutHealth project is to elucidate the potential to modulate the gut microbiome for healthy monogastrics