ESR blog
Kevin Jerez-Bogota & Shiv Vasa
Antimicrobial resistanceMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been… (AMRMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been…) is the ability of a microorganism (e.g., bacteria, viruses, and some parasites) to become resistant to the action of an antimicrobial (like antibiotics, but in essence any substance that can kill or inhibit their growth). This poses a major public health concern, as it means that common infections that were once easily treatable are now increasingly difficult to treat, in both human and veterinary medicine. Research into improving piglet resilience can help us fight antimicrobial resistanceMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been… by reducing the need for antibiotics. Better understanding of nutrition and management practices can lead to improved piglet resilience, reducing the need for antibiotics in early life.
The Invisible Enemy: Battling Antimicrobial Resistance
AMRMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been… is a global issue and has been linked to inappropriate use of antimicrobialsSubstances that are used to either kill or prevent microorganisms from growing and multiplying. (Sou… in humans, animals, and agriculture. In pork production, AMRMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been… has the potential to reduce animal health, increase production costs, and reduce productivity. Antibiotic use in pork production is necessary to prevent, control, and treat diseases. However, when antibiotics are used indiscriminately, or when they are not used appropriately, they can contribute to the emergence of AMRMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been…. According to the European Commission, AMRMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been… causes 35000 deaths[1] in the EU each year and costs the EU €1.5 billion in healthcare costs and productivity losses[2]. Even though the use of all antibiotics as animal growth promoters has been prohibited in the European Union since 2006, efforts to minimize the use of antibiotics in animal husbandry remain ongoing. Consequently, the EU has adopted the Farm to Fork Strategy[3] to help shape the EU’s path towards sustainable food systems. One of the goals of the policy is to reduce the overall use of antimicrobialsSubstances that are used to either kill or prevent microorganisms from growing and multiplying. (Sou… for livestock animals and aquaculture by 50% by 2030, supported by the implementation of two new regulations on veterinary medicines and medicated feed[4]. These regulations provide a range of measures to fight antimicrobial resistanceMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been… and promote responsible use of antimicrobialsSubstances that are used to either kill or prevent microorganisms from growing and multiplying. (Sou… in animals.
The fight against AMR has also brought challenges to the livestock sector. In pig farming for example the cease of use of antibiotics as growth promoters resulted in an increased incidence of postweaning diarrheaA multifactorial enteric disease that affects pigs within two weeks of weaning. This disease is comm… and mortality. To address these challenges, researchers have proposed to use different substances like zinc, copper and prebioticsSelectively fermented ingredients that allows specific changes in the composition or activity of the…, probioticsLive microbial feed supplements, which beneficially affects the host animal by improving its intesti…, phytochemicalsA broad class of bioactive compounds derived from plants. These compounds have a wide range of biolo…, organic acids, and several other feeding strategies to boost animal health and performance. The use of pharmacological levels of Zinc oxide (aka medical zinc, i.e., above nutritional requirement of zinc) has been shown to reduce the incidence of gastrointestinal disorders in pigs and can also increase growth rate and feed efficiencyA cumulative efficiency with which livestock like the pig or the broiler utilizes dietary nutrients …. Thus, following the ban on antibiotic growth promoters, the use of pharmacological zinc oxideAn inorganic compound that is commonly used in animal feed as a zinc source. Zinc oxide has been use… levels in weaners diets became a general practice to reduce the incidence of postweaning diarrheaA multifactorial enteric disease that affects pigs within two weeks of weaning. This disease is comm…. However, in 2017 the European Commission announced a ban of the use of pharmacological levels of zinc oxide in animal feed (allowing a maximum 150ppm), which came into effect in 2022. This ban was set due to the overall benefit-risk balance for medical zinc oxideAn inorganic compound that is commonly used in animal feed as a zinc source. Zinc oxide has been use… is negative due to the risks to the environment outweighing the benefits of preventing diarrhea in pigs[5].
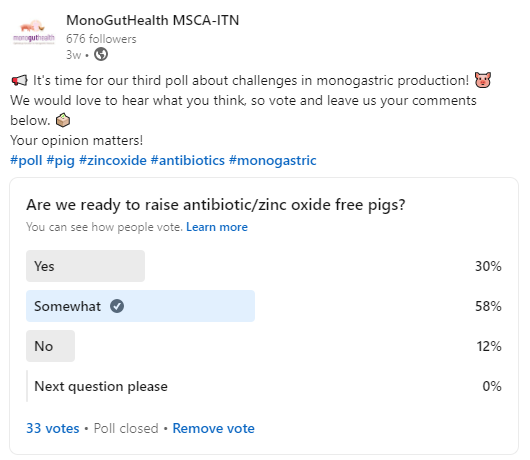
We recently asked to our LinkedIn network: Are we ready to raise antibiotic/zinc oxide free pigs? The results of the poll are in with “Somewhat” being the most popular answer. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in researching alternative ways to raise pigs without the use of antibiotics and zinc oxideAn inorganic compound that is commonly used in animal feed as a zinc source. Zinc oxide has been use….
In the MonoGutHealth project, the PhD students are actively exploring innovative technologies and tools to improve the resilience of piglets and to gain greater insight into the nutritive, microbial, and disease-related factors influencing their early development.
Exploring alternatives
Many consider abrupt weaning to be the most difficult challenge in a pig’s life, as piglets must deal with multiple stressors at the same time. The sudden change from the nutrient rich and highly digestible sow milk to vegetable based feed and mixing of unfamiliar pigs leads to decreased feed intake (Lawlor et al., 2020). This drop causes intestinal enterocytes to starve, impairing gut structure and barrier function. This generally promotes pathogenic bacteria translocation from the gut lumen to the mesenteric lymph nodes and internal organs, resulting in health problems such as diarrhea (Spreeuwenberg et al., 2001; Smith et al., 2010).
One of the commonly used strategies to facilitate the transition to weaning is providing pelleted creep feed to suckling piglets during lactation. However, creep feed intake and number of eaters of creep feed is low in the farrowing rooms, resulting in inconsistent benefit of providing creep feed pre-weaning (Tokach et al., 2020). Since creep feeding is influenced by various factors, there is a scope to stimulate the creep feed consumption and promote gut maturity in piglets. For instance, Shiv Vasa (ESR9 in MonoGutHealth) is investigating whether liquid feeding of creep feed can improve the intake and number of eaters per litter compared to the conventional practice of providing dry pelleted creep feed. Another resort of strategies targets causative agents of postweaning diarrheaA multifactorial enteric disease that affects pigs within two weeks of weaning. This disease is comm…, such as enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETECAn important cause of bacterial diarrhea during the post weaning period in the life of a pig. It is …). These pathogens are a known major contributor to postweaning diarrheaA multifactorial enteric disease that affects pigs within two weeks of weaning. This disease is comm…, and its proliferation can cause diarrhea and even death in severe cases. As such, the main objective of Kevin Jerez’s project (ESR7 in MonoGutHealth) is to develop a new, multicomponent plant-based antibacterial cocktail that would prevent bacterial diseases in the gastrointestinal system of weaned piglets. Both strategies ultimately lead to an increase in the pig’s capacity to deal with weaning stressors and increase their resilience.
Given the intricacy of the weaning process and its associated complications, the project for the ESR10 in MonoGutHealth is attempting to increase our understanding of the impact of the vaginal, fecal, colostrumThe first form of milk produced by sows immediately following birth of piglets. Colostrum has an esp…, milk, udder, environment, and diet microbiota on piglet microbiota development. Similarly, the Ines Garcia (ESR2 in MonoGutHealth) is developing a new tool to extend our knowledge of the small intestinal microbiomeThe diverse consortium of bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, viruses, and their collective genome f… throughout the pig’s life by means of a capsule endoscopy concept. This could enable us to create new microbiota-oriented strategies to augment overall resilience, such as probiotic/prebiotic feeding, improving biosecurity measures, and implementing better management practices.
Take home message
Researching ways to increase piglet resilience through better nutrition and management practices can help reduce the need for antibiotics, which will in turn help us fight antimicrobial resistanceMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been…. Such practices include optimizing sow nutrition, providing effective pre- and postweaning feeding management and targeted nutritional strategies (e.g., feeding antimicrobial plants or probioticsLive microbial feed supplements, which beneficially affects the host animal by improving its intesti…/prebiotics). This can lead to improved piglet resilience and a decrease in the use of antibiotics.
[1] Assessing the health burden of infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU/EEA, 2016-2020. (2022, November 17). European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved January 30, 2023, from https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/health-burden-infections-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria-2016-2020
[2] EU Action on Antimicrobial ResistanceMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been…. (2022, November 17). Public Health. Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://health.ec.europa.eu/antimicrobial-resistance/eu-action-antimicrobial-resistance_en
[3] Farm to Fork Strategy. (n.d.). Food Safety. Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://food.ec.europa.eu/horizontal-topics/farm-fork-strategy_en
[4] Implementation of Regulation (EU) 2019/6 on veterinary medicinal products and Regulation (EU) 2019/4 on medicated feed. (n.d.). Implementation of Regulations. Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://food.ec.europa.eu/animals/animal-health/vet-meds-med-feed/implementation_en
[5] Zinc oxideAn inorganic compound that is commonly used in animal feed as a zinc source. Zinc oxide has been use… – European Medicines Agency. (2018, September 17). European Medicines Agency. Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/veterinary/referrals/zinc-oxide
References
Lawlor PG, Gardiner GE and Goodband RD 2020. 10. Feeding the weaned piglet. The suckling and weaned piglet, 251–275.
Smith F, Clark JE, Overman BL, Tozel CC, Huang JH, Rivier JEF, Blisklager AT and Moeser AJ 2010. Early weaning stress impairs development of mucosal barrier function in the porcine intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298, 352–363.
Spreeuwenberg MAM, Verdonk JMAJ, Gaskins HR and Verstegen MWA 2001. Small IntestineA long tube-like organ that connects the stomach and the large intestine. It helps to digest food co… Epithelial Barrier Function Is Compromised in Pigs with Low Feed Intake at Weaning. American Society for Nutritional Sciences.
Tokach MD, Cemin HS, Sulabo RC and Goodband RD 2020. 5. Feeding the suckling pig: creep feeding. The suckling and weaned piglet, 139–157.
EU Action on Antimicrobial ResistanceMicroorganisms’ ability to withstand antimicrobial treatments. Antibiotic overuse or misuse has been…. (2022, November 17). Public Health. Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://health.ec.europa.eu/antimicrobial-resistance/eu-action-antimicrobial-resistance_en
Farm to Fork Strategy. (n.d.). Food Safety. Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://food.ec.europa.eu/horizontal-topics/farm-fork-strategy_en
Implementation of Regulation (EU) 2019/6 on veterinary medicinal products and Regulation (EU) 2019/4 on medicated feed. (n.d.). Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://food.ec.europa.eu/animals/animal-health/vet-meds-med-feed/implementation_en
Zinc oxideAn inorganic compound that is commonly used in animal feed as a zinc source. Zinc oxide has been use… – European Medicines Agency. (2018, September 17). European Medicines Agency. Retrieved January 19, 2023, from https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/veterinary/referrals/zinc-oxide